Difference between revisions of "Hammer (symbol)"
Tao alexis (talk | contribs) |
Tao alexis (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | The table should be read so that a given hex type and number of hammers would include everything to '''the left and above''' that entry. For example, a type-5 hex with 2 hammers would not only include a gallows, guardpost and so on, but would also include those facilities listed under type-5 with 1 hammer ... and ALSO all the facilities appearing in the type-6 and type-7 columns up to two hammers ... a total of 33 different facilities all told. | + | The table should be read so that a given hex type and number of hammers would include everything to '''the left and above''' that entry. For example, a type-5 hex with 2 hammers would not only include a gallows, guardpost and so on, but would also include those facilities listed under type-5 with 1 hammer ... and ALSO all the facilities appearing in the type-6 and type-7 columns up to two hammers ... a total of 33 different facilities all told. Thus, a type-1 hex with six hammers would have every facility on the table. |
| + | It can be assumed that the number of specific examples of a facility increases with "distance" on the table. Distances should be read according to the Fibonacci series: 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13 and so on, with each new number being the sum of the two previous numbers. | ||
| − | + | A type-1 hex with 5 hammers is 1 hex from a barbican, so it should be assumed that there is still only one of these within the hex. The lighthouse is 2 over and 1 up, for a distance of 3 – this would mean there were 2 lighthouses (the third Fibonacci number above). The gallows is a distance of 7 from our example: this would mean there were 13 gallows in the hex. That number is obviously flexible; we could judge there were between 9 and 13, if it mattered. | |
== Advanced Facilities == | == Advanced Facilities == | ||
Revision as of 00:48, 26 November 2022
- File:Hammers Draganesti.jpg6-mile map of the village Dragasani and surrounding area, showing two hammers in a type-4 hex and one hammer in a type-5.
Hammers are symbols used on game maps to represent the number of accumulated facilities that a given civilised hex has constructed and presently maintains. The number of hammers possessed by a hex is determined by the hex type, which in turn is a product of infrastructure. Hex types range from 1 to 8, with a "1" indicating a highly civilised hex and an "8" indicating uncivilised wilderness. Thus, type-1 and type-2 hexes possess many hammers, while type-7 and type-8 hexes may have none at all.
| Hex Type % |
Hammers Gained | |
|---|---|---|
| Arable | Non-Arable | |
| 7 | 0 | 2 |
| 6 | 1 | 2 |
| 5 | 1 | 3 |
| 4 | 2 | - |
| 3 | 3 | - |
| 2 | 4 | - |
| 1 | 4 | - |
Number of Hammers
Maps in which hammers appear have hexes that possess two designations: arable and non-arable. Arable hexes are primarily farm and pasture land. Non-arable hexes are those exploited for the sake of mining or quarrying. Type-1 to type-4 hexes are always designated as arable; type-5 to type-7 hexes may be arable or non-arable; and type-8 hexes are always treated as non-arable, though some may have the potential to be made arable. Since type-8 hexes don't gain hammers under any circumstances, they are not included on the table shown.
In addition to the hammers added by type, an additional +1 hammer is awarded if the hex includes a sufficiently sized river. A +1 hammer is also given for each settlement a hex includes. This means a type-7 hex might have one hammer, gained from a river, apparently making it equal to a type-6 hex. However, one hammer as it appears in a type-6 hex possesses a superior allotment of facilities by virtue of it being a more civilised hex.
Therefore, it's best not to think of "one hammer" as an isolated quantity. Each hex type may have different number of hammer, depending on its location and inclusion of a settlement. An assignment of "1" hammer may occur in three different hex types. Therefore, the number of hammers AND the hex type must be noted in allotting which facilities the hex includes.
Common Facilities
Facilities are commercial and institutional spaces and constructed establishments designed to facilite an activity, such as inns, dockyards, schools, warehouses, guilds, theatres, palaces, law courts, arsenals and many other places. More complex facilities require a higher level of financial and social commitment to bring into being, often with a large number of persons to operate and maintain; therefore, facility variety depends on the civilisation of the hex. Type-1 hexes have many facilities; type-7 have very few; and type-8 have none at all.
| # Hammers | When Occurring in this Type | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type-7 | Type-6 | Type-5 | Type-4 | Type-3 | Type-2 | Type-1 | |
| 0 | farm | 1 hammer minimum | 2 hammers minimum | 3 hammers minimum | 4 hammers minimum | ||
| 1 | boat dock, garner, hovel, ox tether, sawpit, thorp, watermill for grain, well | cloth mill, gong pit, hamlet, shearing station, windmill, winepress | bakery, carter post, granary, gravesites, irrigation pump | ||||
| 2 | carter post, gong pit, shearing station | bakery, granary, gravesites, irrigation pump, shrine | gallows, guardpost, way station | cemetery, cottagecrafting, day market, hostel, manor, quay, storehouse, tabernacle, village | |||
| 3 | 2 hammers maximum | cottagecrafting, guardpost, storehouse, way station | day market, hostel, quay, shaft mine | blacksmith, block house, chapel, gamewarden | barracks, demesne, glebe, inn, public house, warehouse, wharf, workshops | ||
| 4 | 3 hammers maximum | demesne, inn, public house | keep, lighthouse | estate, garrison, monastery, quarry, temple | stockyard, town hall | ||
| 5 | 4 hammers maximum | gatehouse | barbican, monolith/stele | palace, wholesale market | |||
| 6 | 5 hammers maximum | basilica, foundry | grocer, harbour, library | ||||
The table should be read so that a given hex type and number of hammers would include everything to the left and above that entry. For example, a type-5 hex with 2 hammers would not only include a gallows, guardpost and so on, but would also include those facilities listed under type-5 with 1 hammer ... and ALSO all the facilities appearing in the type-6 and type-7 columns up to two hammers ... a total of 33 different facilities all told. Thus, a type-1 hex with six hammers would have every facility on the table.
It can be assumed that the number of specific examples of a facility increases with "distance" on the table. Distances should be read according to the Fibonacci series: 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13 and so on, with each new number being the sum of the two previous numbers.
A type-1 hex with 5 hammers is 1 hex from a barbican, so it should be assumed that there is still only one of these within the hex. The lighthouse is 2 over and 1 up, for a distance of 3 – this would mean there were 2 lighthouses (the third Fibonacci number above). The gallows is a distance of 7 from our example: this would mean there were 13 gallows in the hex. That number is obviously flexible; we could judge there were between 9 and 13, if it mattered.
Advanced Facilities
In addition to the above, there are even larger establishments that may exist within a given settlement. Large settlements with a population of more than 5,000 may also count the hammer-points within a radius of one hex. A settlement with a population of 25,000 may count all the hammer points without two hexes.
| Hammer Symbol | Points |
|---|---|
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 3 |
| 3 | 7 |
| 4 | 15 |
| 5 | 31 |
| 6 | 63 |
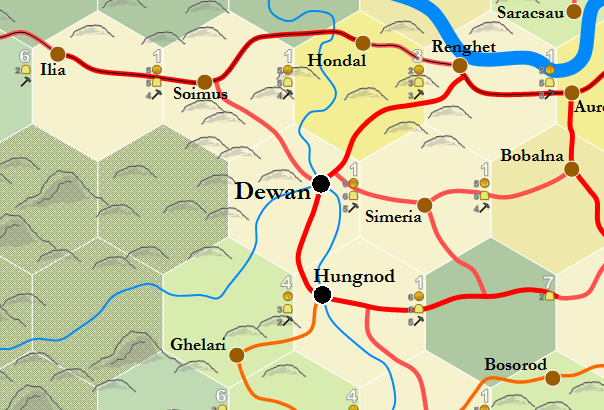
For example, the town of Dewan in Transylvania has a population of 5,832. This means that it can count the hammers in those hexes occupied by Soimus, Hondal, Simeria, Hungnod and Ghelari. The sixth hex is a wilderness and, while technically counted, contributes nothing to Dewar's total.
The hammers that exist are counted in a peculiar fashion, as shown on the Hammer Counting table. Thus, Dewan receives 31 points from it's own hex, 15 from Soimus, 7 from Hondal, 15 from Simeria, 31 from Hungnod and 3 from Ghelari. This totals 102. If Dewan were an even larger city, it would be able to count additional hammers from sources two hexes away, such as Ilia, Renghet and Bobalna. Bosorod is three hexes away and couldn't be counted in any case.