Difference between revisions of "Egyptian History"
Tao alexis (talk | contribs) |
Tao alexis (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
Advanced [[Construction (technology)|construction]] techniques became highly precise and sophisticated, showcasing the Egyptians' mastery of geometry and engineering. Quarrying techniques enabled extraction of limestone and granite; irrigation systems that used canals and dikes to manage water flow. Other advancements included the use of bas-relief and the use of proportion and perspective; production of intricate statues and sculptures; and accurate surveying and land measurement techniques. This allowed the measurement and demarcation of land boundaries, despite wide-spread flooding of the Nile every year. | Advanced [[Construction (technology)|construction]] techniques became highly precise and sophisticated, showcasing the Egyptians' mastery of geometry and engineering. Quarrying techniques enabled extraction of limestone and granite; irrigation systems that used canals and dikes to manage water flow. Other advancements included the use of bas-relief and the use of proportion and perspective; production of intricate statues and sculptures; and accurate surveying and land measurement techniques. This allowed the measurement and demarcation of land boundaries, despite wide-spread flooding of the Nile every year. | ||
| − | The decline of Old Kingdom culminated in political and economic collapse after 2300 <small>B.C.</small>. Central power waned, while regional authorities gained strength, until Egypt collapsed into a disorganized feudalism that lasted almost four centuries. | + | The decline of Old Kingdom culminated in political and economic collapse after 2300 <small>B.C.</small>. Central power waned, while regional authorities gained strength, until Egypt collapsed into a disorganized feudalism that lasted almost four centuries. Two dynasties, the 7th and 8th, occur during this chaos. |
| + | |||
| + | == Middle Kingdom == | ||
| + | Lasting from 2143-1790 <small>BC</small>, comprising the 9th to 12th dynasties. From '''Thebes''', through the Middle Kingdom's first three dynasties, Egypt progressed a great distance towards reunification. Under '''Amenemhet''' and Sesotris I, the 12th Dynasty disciplined the oligarchic nobility. Building projects were undertaken, at El-Lisht and Karnak. An expedition into Nubia secured Egypt's southern borders above the 1st cataract of the Nile, a series of rocky rapids and waterfalls, where the river's flow is disrupted. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Karnak.jpg|left|350px|thumb|Karnak, begun during the reign of Senusret I (1920-1875 <small>B.C.</small>) during the Middle Kingdom]] | ||
| + | Shipbuilding techniques were developed, riverboats and barges, allowing improved navigation of the Nile. Improvements were made in monumental architecture: statues, obelisks and temple construction, as well as colonnades, pylon gateways and papyrus columns. Depicted human forms grew more realistic. There were advancements in casting and alloying, in decorative pottery and in spinning and weaving cloth. Trade with Syria and Nubia increased in volume, while Egyptian merchants began to appear along the Red Sea. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Sesotris III''' (1887-1849 <small>BC</small>) carried Egyptian standards into Syria; thereafter he established a series of fortresses along Egypt's eastern border and into the Levant — called the "Ways of Horus." These were intended to exert greater control over strategic routes. Yet this was the Middle Kingdom's zenith; corruption and declining agricultural produce would weaken Egypt over the sixty years. By then, foreign populations, such as the '''Hyksos''', began to threaten. As succession disputes disrupted the social fabric and stability of Egypt, the Hyksos succeeded in gaining control over much of the region in what's called the '''Second Intermediate Period'''. | ||
Revision as of 22:48, 20 August 2023
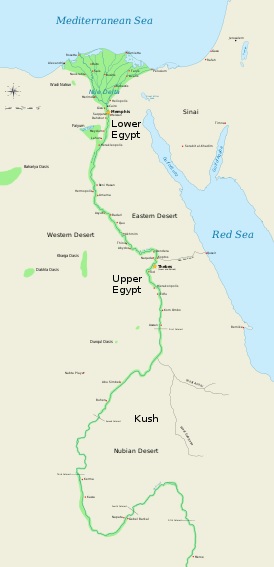
Egyptian History is defined by the Nile Valley, not occupied by man until after the last Ice Age. The Sahara plateau, formerly an enormous grassland, began to dry and suffer from desertification, driving humans and animals from northern Africa toward the Mediterranean coast or eastward to the banks of the Nile. In the Paleolithic, these lived on high cliffs above the valley; but their successors, the agriculturalists of the Neolithic, descended to the valley floor to plant their crops. The ebb and flow of the Nile each season would flood the land with rich deposits of mud, making it a rich land for agriculture; thus the pattern of the river would dominate every part of Egyptian culture.
By that time, there were perhaps 40 agricultural communities, strung together like beads along the ribbon of the Nile River north of the First Cataract. By about 5000 BC, Egypt had been unified to some extent into two kingdoms: one in the delta (Lower Egypt) and one in the valley (Upper Egypt). The period saw the emergence of the many cultural, social and technological foundations that would later define the Ancient Egyptian civilisation. After many centuries of warfare in the Chalcolithic period, the two kingdoms were unified under King Menes, also called Narmer, who established Memphis as his capital, in the northern part of the Nile Valley. Thus was established the 1st Dynasty of Egypt.
Early Dynastic Period
Lasting from 3200 to 2800 BC, the period represents the dawn of the pharaonic civilisation. Its rulers established a centralised state, solidifying the power of the pharoahs while establishing a bureaucratic system to manage the affairs of the state and its regional governors and officials. Heiroglyphic writing flourished, while the pharoahs built elaborate royal tombs for themselves. Agriculture flourished as the backbone of the economy, paving the way for trade and artisanship.
Religion played a central role. The pharoah was considered a divine figure, who in fact received messages from the Gods (a similar thing was taking place in Mesopotamia). Temples and religious practices reacted to a polytheistic enlightenment that followed. Yet the will of man contended against the will of the new Gods, so that an era of unrest occurred that laid the foundation for the Old Kingdom.
Old Kingdom
Lasting from 2780-2270 BC, comprising the 3rd to 6th dynasties. The capital remained at Memphis. The period includes the most famous of pyramid builders of the 4th Dynasty: Zoser (Djoser) of the 3rd Dynasty, whose step pyramid was constructed at Saqqara, and Cheops (Khufu), Chephren (Kha-ef-Re) and Mycerinos (Men-kau-Re) of the 4th Dynasty, whose pyramids still stand at Gizeh. These pyramids are not only symbolic; they're also indicative of the power and wealth of the 4th Dynasty rulers. The huge funds lavished upon these royal burial chambers were responsible for the gradual weakness and decline of the Old Kingdom, which became more apparent in the time of the 5th and 6th Dynasties.
Advanced construction techniques became highly precise and sophisticated, showcasing the Egyptians' mastery of geometry and engineering. Quarrying techniques enabled extraction of limestone and granite; irrigation systems that used canals and dikes to manage water flow. Other advancements included the use of bas-relief and the use of proportion and perspective; production of intricate statues and sculptures; and accurate surveying and land measurement techniques. This allowed the measurement and demarcation of land boundaries, despite wide-spread flooding of the Nile every year.
The decline of Old Kingdom culminated in political and economic collapse after 2300 B.C.. Central power waned, while regional authorities gained strength, until Egypt collapsed into a disorganized feudalism that lasted almost four centuries. Two dynasties, the 7th and 8th, occur during this chaos.
Middle Kingdom
Lasting from 2143-1790 BC, comprising the 9th to 12th dynasties. From Thebes, through the Middle Kingdom's first three dynasties, Egypt progressed a great distance towards reunification. Under Amenemhet and Sesotris I, the 12th Dynasty disciplined the oligarchic nobility. Building projects were undertaken, at El-Lisht and Karnak. An expedition into Nubia secured Egypt's southern borders above the 1st cataract of the Nile, a series of rocky rapids and waterfalls, where the river's flow is disrupted.
Shipbuilding techniques were developed, riverboats and barges, allowing improved navigation of the Nile. Improvements were made in monumental architecture: statues, obelisks and temple construction, as well as colonnades, pylon gateways and papyrus columns. Depicted human forms grew more realistic. There were advancements in casting and alloying, in decorative pottery and in spinning and weaving cloth. Trade with Syria and Nubia increased in volume, while Egyptian merchants began to appear along the Red Sea.
Sesotris III (1887-1849 BC) carried Egyptian standards into Syria; thereafter he established a series of fortresses along Egypt's eastern border and into the Levant — called the "Ways of Horus." These were intended to exert greater control over strategic routes. Yet this was the Middle Kingdom's zenith; corruption and declining agricultural produce would weaken Egypt over the sixty years. By then, foreign populations, such as the Hyksos, began to threaten. As succession disputes disrupted the social fabric and stability of Egypt, the Hyksos succeeded in gaining control over much of the region in what's called the Second Intermediate Period.